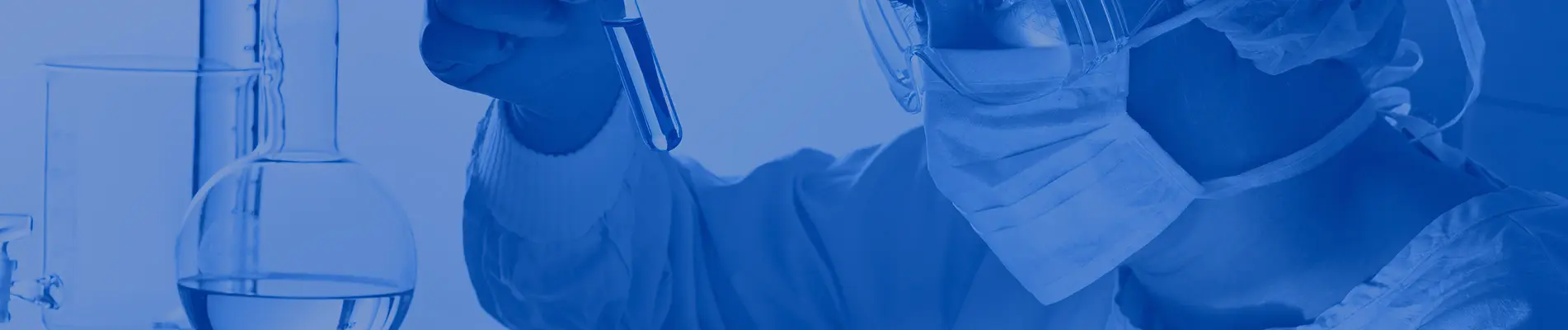

10 Essential Tips for Using Polyamide Hot Melt Adhesive Effectively?
Polyamide Hot Melt Adhesive is increasingly becoming a favorite in various industries. According to a recent report by Smithers Pira, the demand for hot melt adhesives is projected to grow by 5.2% annually. This growth is driven by advancements in material technology and the push for more sustainable products. Polyamide adhesives stand out due to their excellent thermal stability and adhesion properties.
Use of Polyamide Hot Melt Adhesive differs across sectors, from automotive to packaging. For instance, the automotive industry values its ability to bond dissimilar materials effectively. However, not all applications exploit the full potential of these adhesives. Mistakes in temperature control or surface preparation can lead to failures. It’s essential to understand the nuances of Polyamide Hot Melt Adhesive for optimal performance.
As manufacturers strive for efficiency, they often overlook critical factors. Many fail to consider the right application techniques. Successful use hinges on proper equipment and adhesive storage. Education on Polyamide Hot Melt Adhesive can solve these issues, leading to better product outcomes and enhanced safety standards. Understanding these challenges is crucial to maximizing the benefits of this versatile adhesive type.

Understanding Polyamide Hot Melt Adhesive Properties
Polyamide hot melt adhesive (PHMA) is known for its versatility. It has excellent thermal resistance and can withstand high temperatures. This adhesive can bond various substrates like plastics, metals, and textiles. Its strong adhesion is particularly beneficial in challenging applications. However, you must understand its properties to use it effectively.
One key aspect of PHMA is its high elasticity. This allows for flexibility in bonding, especially in dynamic joints. But sometimes, that elasticity can lead to weaker bonds under specific conditions. Another consideration is its adhesion to different materials. Some surfaces may require surface treatment for optimal results. Testing the bond strength before full application is often necessary.
Temperature control is crucial when working with PHMA. The adhesive must be heated properly to ensure optimal flow and adhesion. Too low a temperature can result in poor bonding. Similarly, applying it too thickly can lead to inefficient adhesion. It’s important to find that perfect balance. Regular evaluations of the adhesive's performance can help identify potential issues early on.
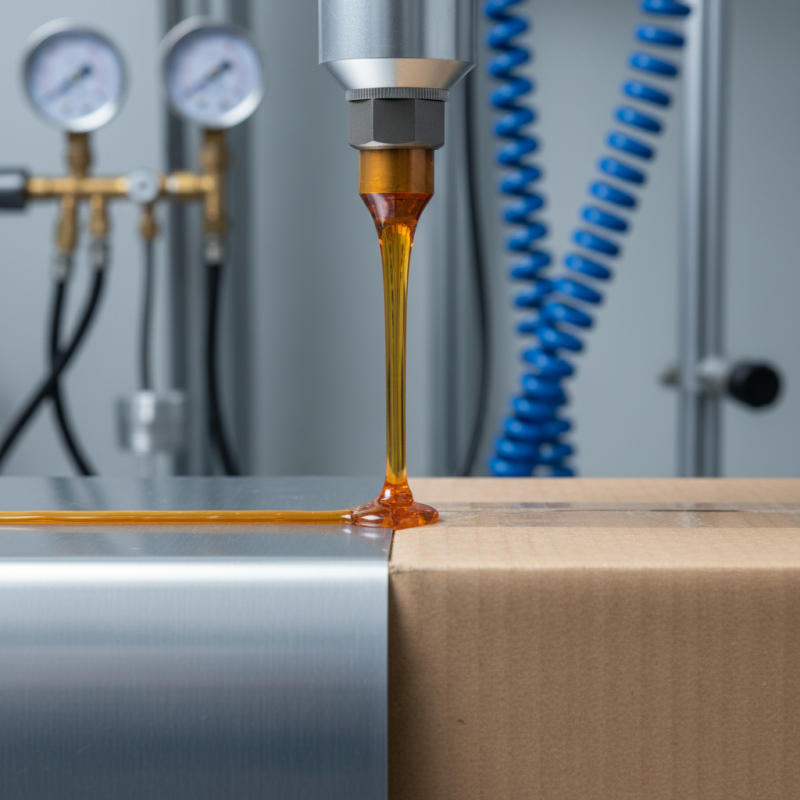
Choosing the Right Application Method for Polyamide Adhesives
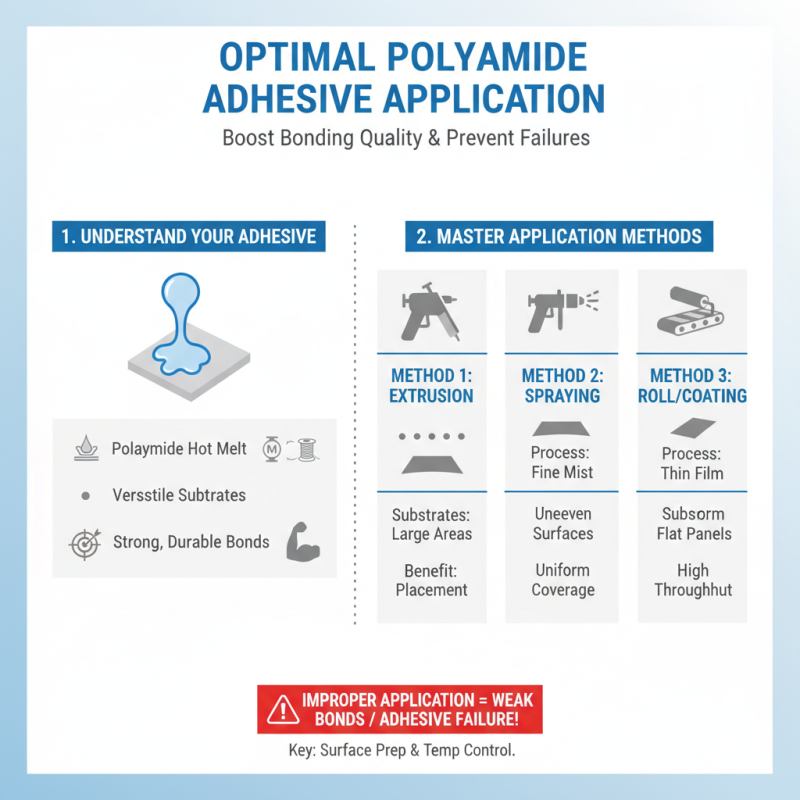
Choosing the right application method for polyamide adhesives can significantly impact bonding quality. Polyamide hot melt adhesives are versatile. They work well on various substrates like plastics, metals, and textiles. However, improper application can lead to weak bonds or even adhesive failure.
One important tip is to consider the surface preparation. Clean surfaces ensure optimal adhesion. Dirt, grease, or moisture can compromise bond strength. In fact, a study shows that surface contaminants can reduce adhesion strength by up to 50%. Proper surface treatment can elevate the performance of these adhesives.
Temperature is crucial when using polyamide adhesives. They should be applied at the recommended melting temperature. Too high a temperature can degrade the adhesive, while too low can lead to inadequate bonding. Check the adhesive’s specifications for ideal conditions. Balance is key here. Uncontrolled temperatures often result in unreliable bonds, leading to costly repairs.
Using the right dispensing method also matters. Whether you choose a glue gun, nozzle, or roller, ensure it fits the project needs. For intricate work, a precise nozzle may be better. Larger surfaces might benefit from rollers for even distribution. Sometimes, experimentation is necessary to find the best fit.
Surface Preparation for Optimal Adhesive Bonding
Surface preparation is crucial for achieving optimal bonding with polyamide hot melt adhesives. According to industry studies, around 60% of adhesive failures stem from inadequate surface treatment. Properly cleaned and prepared surfaces enhance adhesion by allowing the adhesive to form a stronger bond.
One tip is to clean surfaces thoroughly. Use isopropyl alcohol or similar solvents to remove dust, oil, and other contaminants. Make sure the surface is completely dry before applying the adhesive. Another important aspect is roughening the surfaces slightly. This can increase surface area for better penetration and adhesion. Studies indicate that roughened surfaces can increase bond strength by up to 25%.
Evaluate your preparation process regularly. If bonds fail, it may be time to reassess surface treatment methods. Not all surfaces react predictably with adhesives. For example, some plastics may require specific primers for improved adhesion. Testing small samples before full-scale application can save time and resources.
Temperature Control Techniques for Effective Adhesive Use
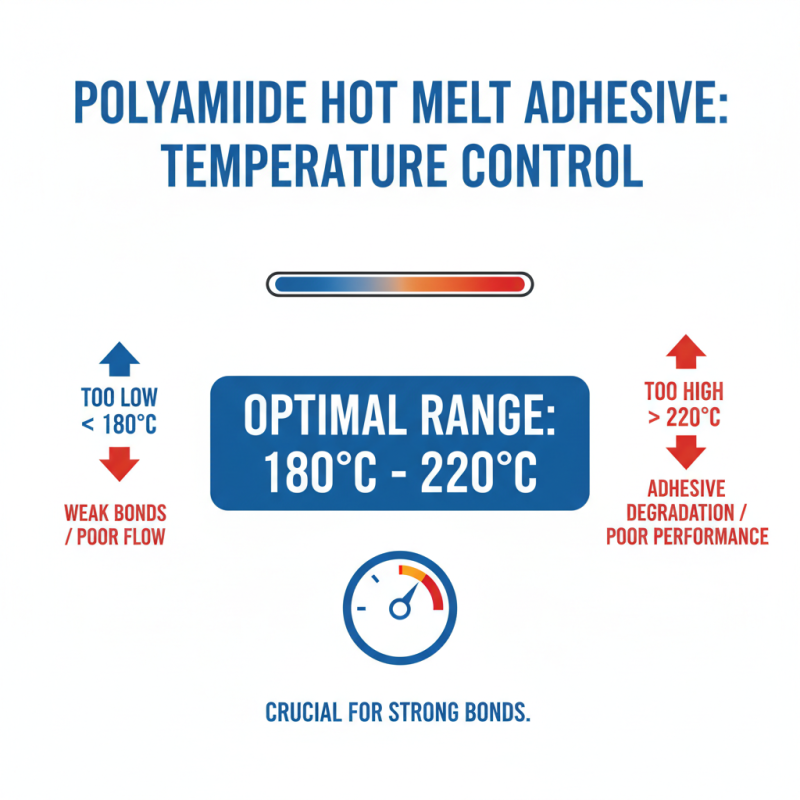
Temperature control is crucial when using polyamide hot melt adhesive. The optimal temperature range for melting this adhesive typically falls between 180°C to 220°C. If the temperature is too low, the adhesive won't flow properly. This can lead to weak bonds. Conversely, excessive heat may degrade the adhesive, resulting in poor performance.
Research shows that maintaining temperature stability impacts adhesive effectiveness significantly. According to industry reports, a 5°C variation can alter bond strength by up to 20%. It's vital to monitor temperature closely. Many professionals recommend using thermometers and thermal imaging to track changes in real-time. Adjustments should be made swiftly, especially in high-production environments.
Employing a pre-heating stage might offer additional benefits. This allows the adhesive to achieve an even viscosity before application. However, this approach requires careful consideration. Overheating during pre-heating can lead to char formation, affecting the final product's aesthetics and durability. Regular calibration of heating equipment is also necessary to prevent discrepancies. Balancing heat with efficiency is an ongoing challenge for many operators.
Post-Application Care and Maintenance for Long-lasting Adhesives
After applying polyamide hot melt adhesive, proper care is crucial for longevity. The adhesive needs time to cure fully. Typically, it requires 24 hours for optimal bonding. Some might rush this process, leading to weak joints.
Environmental factors play a significant role. Humidity levels affect adhesion performance. Studies show that adhesives exposed to high humidity can lose up to 30% of their strength. Regular checks on the bonding surface can help identify any failures early.
Cleaning tools and surfaces immediately after application can prevent contamination. Residual adhesive can compromise future applications. A solution containing isopropyl alcohol can be effective. Proper storage of unused adhesive is also essential. Keeping it in a cool, dry place can extend its shelf life significantly. Remember, attention to these details can mean the difference between success and failure.
10 Essential Tips for Using Polyamide Hot Melt Adhesive Effectively
| Tip Number | Tip Description | Post-Application Care | Maintenance Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ensure proper surface preparation | Keep surfaces clean and dry | Immediately after application |
| 2 | Apply at the correct temperature | Avoid overheating | Ongoing |
| 3 | Use the right amount of adhesive | Monitor joint integrity | After initial cure |
| 4 | Control the application speed | Check for even distribution | Initial setup |
| 5 | Allow adequate curing time | Store in appropriate conditions | 24-48 hours |
| 6 | Use suitable substrates | Regularly inspect bonding | As needed |
| 7 | Avoid moisture exposure | Dry environment is essential | Ongoing monitoring |
| 8 | Consider environmental factors | Evaluate temperature and humidity | Continuous evaluation |
| 9 | Test bonds before mass production | Assess joint strength regularly | Prior to production |
| 10 | Educate your team on adhesive use | Conduct regular training sessions | Ongoing |
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Best Polyamide Hot Melt Adhesive for Your Projects
-

How to Effectively Use PUR Hot Melt Adhesive for Your Projects
-

What is Polyester Hot Melt Adhesive and Its Key Applications
-

Top Uses and Benefits of PUR Hot Melt Adhesive in 2025
-

How to Choose the Best Beer Bottle Labeling Adhesives for Your Brewery
-
What is Crylate Adhesive? Understanding Its Uses and Benefits
